Do you know how to check the Python version you are using? This tutorial provides you with 10 different ways to check the Python version. Now, you may ask why use code and 10 different methods. It is because we are programmers and we like our code to do the tasks. It is not only easy and simple but also creative.
- Different Ways to Check Python Version with Full Code
- 1. Using the platform module
- 2. Using the sys module
- 3. Using the subprocess module to check the Python version
- 4. Using the pkg_resources module
- 5. Using the __version__ attribute to check the Python version
- 6. Using the python3 command-line tool
- 7. Using sysconfig module and os.path.join
- 8. Using the PYTHONHOME environment variable
- 9. Using the sys.executable attribute
- 10. Using the site module to check the Python version
- Conclusion
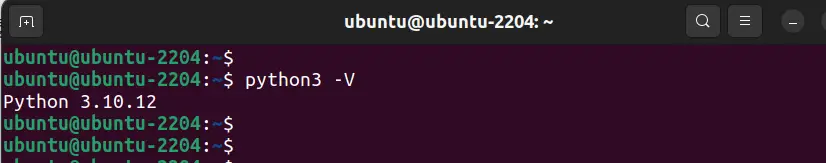
However, let’s not leave the most basic way which is to use the terminal to check the Python version. You just need to issue the following command to show the Python version:
Different Ways to Check Python Version with Full Code
Now, review the 10 different methods to check the Python version with fully working code examples. You may reuse the code, and add it to your DevOps scripts, or in your applications.
1. Using the platform module
The platform module is a built-in module that provides information about the underlying platform, including the Python version. Here’s a simple example to check the Python version:
import platform
python_version = platform.python_version()
print(python_version)This code will print the Python version, for example:
3.10.132. Using the sys module
The sys module is a built-in module that provides access to system-specific parameters and functions, and it contains a version attribute that holds the Python version. Here’s a simple example:
import sys
python_version = sys.version
print(python_version)This code shows the Python version, including the release level and serial number. For instance:
3.10.13 (main, Mar 14 2023, 23:21:36) [1] 64-bit3. Using the subprocess module to check the Python version
The subprocess module lets you run shell commands. You can use it to execute the ‘python’ command-line tool and retrieve the Python version.
import subprocess
process = subprocess.Popen(['python3', '--version'], stdout=subprocess.PIPE)
output, _ = process.communicate()
python_version = output.decode('utf-8').strip()
print(python_version)This code prints the Python version. For instance:
Python 3.10.134. Using the pkg_resources module
The pkg_resources module helps access details about installed packages. You can use it to fetch the version of the matplotlib package, which aligns with the Python version.
import pkg_resources
matplotlib_version = pkg_resources.get_distribution('matplotlib').version
print("Matplotlib version:", matplotlib_version)This code will print the Python version, for example:
3.5.15. Using the __version__ attribute to check the Python version
The __version__ attribute is a common attribute of Python modules, including the matplotlib module itself. This method can be used to access the Python version directly from the module.
import matplotlib
matplotlib_version = matplotlib.__version__
print("Python version:", matplotlib_version)This code will print the Python version, for example:
3.5.16. Using the python3 command-line tool
The python3 command-line tool can be used to execute Python scripts. This method can be used to get the Python version by running the python3 command with the --version flag.
import os
command = 'python3 --version'
output = os.popen(command).read()
python_version = output.strip()
print(python_version)This code lists the current Python version, for example:
Python 3.10.67. Using sysconfig module and os.path.join
We can also check the Python version by combining sysconfig and os.path.join. Let’s display the Python version and the executable path.
import sysconfig
import os
try:
print("Python version")
print(sysconfig.get_python_version())
executable_path = sysconfig.get_path('executable')
if executable_path:
print("Executable path")
print(os.path.realpath(executable_path))
except KeyError:
pass # Do nothing if 'executable' key is not present
except Exception as e:
print(f"An unexpected error occurred: {e}")This code will print the Python version, for example:
Python 3.108. Using the PYTHONHOME environment variable
The PYTHONHOME environment variable specifies the location of the Python installation. This method can be used to get the Python version by extracting the version number from the path to the Python executable.
import sys
python_version = sys.version.split(' ')[0]
print("Python version:", python_version)This code will print the Python version, for example:
Python version: 3.10.69. Using the sys.executable attribute
The sys.executable attribute contains the path to the Python executable. This method can be used to get the Python version by extracting the version number from the path to the Python executable.
import sys
import re
python_executable = sys.executable
# Extract Python version from the executable path using regex
match = re.search(r'python(\d+(\.\d+)*)', python_executable)
python_version = match.group(1) if match else "Unknown"
print("Python version:", python_version)This code will print the Python version, for example:
310. Using the site module to check the Python version
The site module provides access to site-specific Python configuration. This method can be used to get the path to the Python installation, which can then be used to extract the Python version.
import site
import sys
import platform
# Get the site-packages path
python_path = site.getsitepackages()[0]
# Extract Python version from the path
python_version = python_path.split('/')[-1]
# Print Python version
print(f"Python version: {python_version}")
# Additional information using sys and platform
print(f"Python version (sys): {sys.version}")
print(f"Python version (platform): {platform.python_version()}")This code will print the Python version, for example:
Python version: dist-packages
Python version (sys): 3.10.6 (main, Nov 14 2022, 16:10:14) [GCC 11.3.0]
Python version (platform): 3.10.6Conclusion
We hope you would have got the desired help from the above code examples. The purpose of this tutorial is also to show how easily you can achieve the same thing in many different ways. Also, Python has a vast set of features that we want you to explore. Once you are aware of a technique it is much easier to use it somewhere else as well. Just be mindful of the pros and cons of each approach before using it.
Happy Coding!






