In this Python programming class, we’ll cover the list append method, its purpose, syntax, flowchart, and examples. Please note that the lists are the main constructs to implement a sequence in Python.
Introduction to List Append()
Good Morning, we wish you had a great day. Today, we will discuss a list method known as Append in Python. It is one of the essential methods that you learn in a short while.
Before reading this tutorial, please polish your knowledge of Lists in Python. We will be teaching according to the Python 3 syntax. If required, you may modify them for other versions.
List Append()
This method allows us to append an item to a list, i.e., insert an element at the end. It is a built-in method in Python. It is one of the methods along with the extend() method which can modify a list.
Syntax
To call it, you need to use the following syntax.
list.append(item or object)
The object can be of any type, i.e., list, element, dictionary, numbers, strings, alphanumeric characters, etc.
It modifies the original list by adding an item to the end of the list. It does not have a return value.
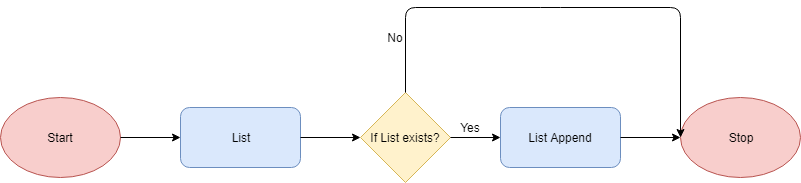
Workflow
This method is meant only for lists. It primarily takes an item from the user and adds it to the end of the list.
The below flowchart demonstrates the functioning of this method:
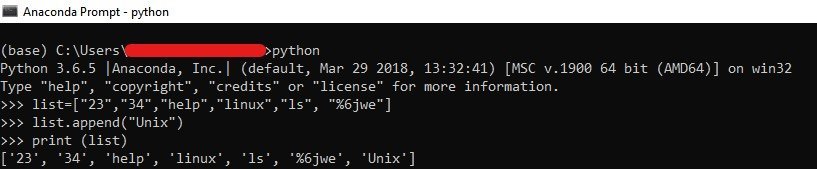
Here is a sample program to show how to use it:
List = ["23", "34", "help", "linux", "ls", "%6jwe"]
List.append("Unix")
print (List)The below image shows the output:
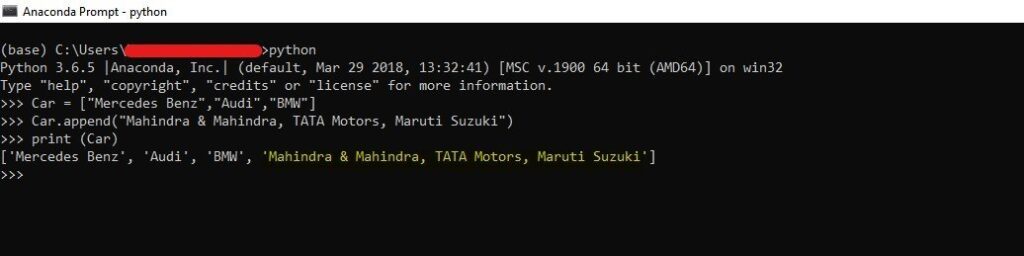
Examples
Append an Element to the List
Car = ["Mercedes Benz", "Audi", "BMW"]
Car.append("Mahindra & Mahindra, Maruti Suzuki, TATA Motors")
print (Car)The output of the above program is as follows.
Append a List to a List
color = ["orange", "blue", "green"] rainbow = ["purple", "teal", "cyan"] color.append(rainbow) print (color)
The output of the above program is as follows.
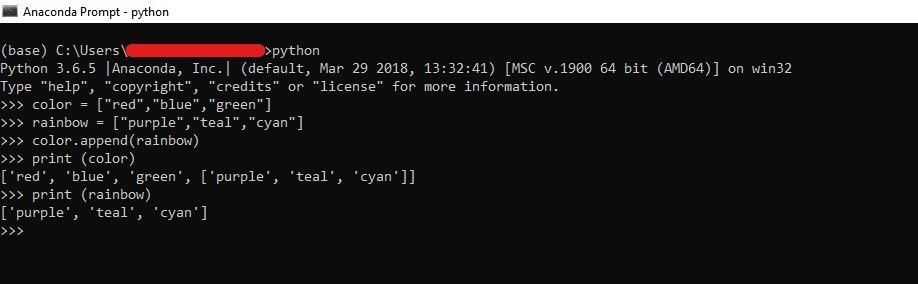
The difference between outputs after appending an element to a list and list to a list is the way access takes place.
In the above example, to access blue in the updated color list, we can type “print (color[1])” whereas if we want to access purple, we need to issue the “print (color[3][0])” command.
Time Complexity
The time complexity is O(1) which means that the List Append method has a constant interval of time for each input it appends to a list.
It does not consider the different amounts of time for different inputs. Lastly, our site needs your support to remain free. Share this post on social media (Linkedin/Facebook) if you gained some knowledge from this tutorial.
Enjoy coding,
TechBeamers.