From this tutorial, you will learn about the Python list Clear method. You will see how to apply it to sequences with the help of examples.
Introduction to Python List Clear()
The clear() method performs the remove operation on a list and removes all the elements. Its syntax is as follows:
Note: The syntax used in the below section is for Python 3. You can change it to any other version of Python.
List Clear()
If you want to clear a list instantly in your Python program, this is the method you should call.
To Learn about Lists – Read Python List
Syntax
The following is the syntax to call this method.
List_name.clear()
After the clear() method gets called, your list gets empty. It doesn’t return any value.
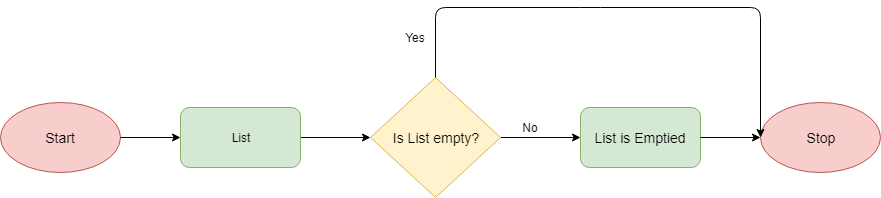
Workflow
Numerous alternative techniques exist for effectively emptying a Python list. Nevertheless, the Clear method offers a straightforward means of accomplishing this task.
This method operates without the need for any arguments and efficiently wipes out the entire contents of the list. Subsequently, the list is reset to a pristine, empty state.
Below is a visual representation of the process in the form of a flowchart:
Python’s del method
We can achieve the same objective using Python’s del method. It has the following syntax.
del List_name[:]
See this example.
# Initialize a list
listtoclear = [{'a', 'x'}, (1), [3.5, (1, 2)]]
# clearing the list
del listtoclear[:]
print('List after clear():', listtoclear)Below is the output after executing the above code.
List after clear(): []
You can see that the clear() method has better semantics than the del . And, it is a bit easy to use.
Examples
Here are some examples to help you use the list clear() method in your Python programs.
Clear a list containing numbers
Fibonacci = [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8] Fibonacci.clear() print (Fibonacci)
Output:
[]
Clear a list containing strings
Linux_distro = ["Ubuntu OS", "Linux Mate OS", "Elementary OS", "Debian OS", "Kali Linux OS"] Linux_distro.clear() print (Linux_distro)
Output:
[]
Clear a list having random values
Random = ["Google", 45, "Dolphin", 23, 21] Random.clear() print (Random)
Output:
[]
Key Facts
Here is a table summarizing some important facts about the list clear() method in Python in point form:
| Fact | Description |
|---|---|
| The list clear() method removes all the elements from a list. | It does not take any arguments and returns no value. |
| The clear() method can be used to empty a list. | This can be useful if you no longer need the elements in the list. Or if you want to start fresh with a new list. |
| The method can be used on any list, regardless of size or content. | This means that it permanently removes the elements from the list. |
Also Read: Add Elements using Python List Insert()
When should be using the list clear() in Python
Here are some unique examples or problems where the list.clear() method can be useful:
- Clearing a list after you finish using it: This is a good way to avoid memory leaks. A memory leak occurs when you create an object but do not delete it when it is no longer in use. This can cause your program to use more and more memory, eventually leading to a crash.
- Starting fresh with a new list: If you need to start fresh with a new list, you can use the list.clear() method to clear the old list and create a new one.
- Removing all the elements from a list before you add new elements: This becomes useful if you expect the new elements at the beginning of the list.
- Emptying a list before you delete it: This can be useful if you want to avoid errors. If you delete a list that contains elements, Python will raise an error. By emptying the list first, you can avoid this error.
We hope this helps! Let us know if you have any other questions.
Lastly, our site needs your support to remain free. Share this post on social media (Linkedin/Facebook) if you gained some knowledge from this tutorial.
Enjoy coding,
TechBeamers.