This guide will teach you how to find the index of an element in a Python list. You will learn how to use the list.index() method with practical examples.
Please note that the code examples provided below follow Python 3 syntax. You can adapt them to different Python versions as needed.
Python List Index
To Learn about Lists – Read Python List
List Index Method
The Index function is a built-in list method that allows you to find out the index or position of an element in a sequence. In other words, this method searches for an element in the list and returns its index.
The list index() method takes three arguments: the element you want to find, and the optional (start, end) index. Its syntax is as follows:
located_at = List_name.index(element, start_pos, end_pos)
The start index is optional and defaults to 0. If the element is found, the method returns its index. If the element is not found, the method raises a ValueError exception.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
Parameterselement | The list element we want to find. |
start_pos | It is optional and refers to the position where the search begins. |
end_pos | It is also optional and specifies the position where the search has to end. |
Return valuelocated_at | An integer value refers to the position of the element found in the list. |
ErrorValueError | When the list index method fails to find the element, it throws the ValueError. |
Also read: How to extend a list in Python
Please note that you can provide any input such as a list, a tuple, or a substring. See the below example.
>>> myList = ['1', '11', 1, 'a', 'x', 1.1]
>>> myList.index(1)
2
>>> myList.index('x')
4How does the Python list Index() function work?
It takes one input which is the element for which you want the index or position as the output.
This method searches for the element in the list and returns the index that matches its value else raises the ValueError error.
While searching for substrings, it raises the following error.
"Substring not found"
>>> first = 'Python is the language of the future.'
>>> print(first.index('lang', 10))
14
>>> print(first.index('invalid', 10))
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#34>", line 1, in <module>
print(first.index('invalid', 10))
ValueError: substring not found
>>>The flowcharts below attempt to explain the flow of the list index in Python:
For elements in the list:
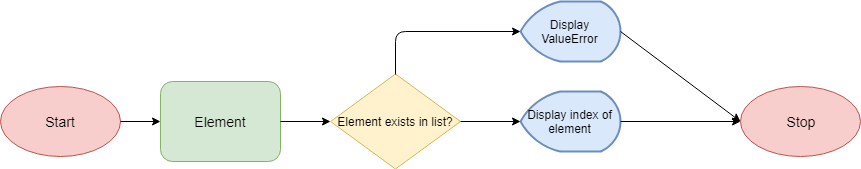
For characters in the string:
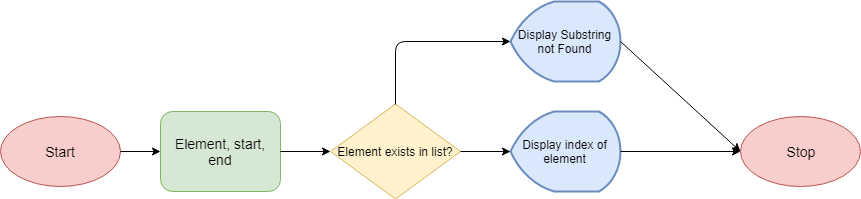
Program Examples
Here are some examples of code calling the Python list index method. Practice with these as much as you can to excel in Python programming skills. In case, you feel to train more, try our 40 Python exercises.
Using the wrong element
myList = [2,3,4,5,6] myList.index(1)
The output is:
Traceback (most recent call last): File "C:\Python\Python35\test.py", line 3, in <module> myList.index(1) ValueError: 1 is not in list
Find the element index in a tuple
myList = [2,3,(3,4),5] print(myList.index((3,4)))
The result is:
2
Key Facts
Here are important facts about the Python list index() method presented in the table below:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | index() method |
| Purpose | To find the index (position) of the first occurrence of a specified element in a list. |
| Input | Accepts a single argument, the element to search for in the list. |
| Output | Returns the index (position) of the first occurrence of the element. |
| Search Behavior | Searches the list from the beginning to find the first match. If not found, raises a ValueError. |
| Optional Parameters | Can take optional parameters for specifying a starting and ending index for the search. |
| Indexing Starts at 0 | The first element in the list has an index of 0, the second has an index of 1, and so on. |
| Error Handling | Raises a ValueError if the specified element is not found in the list. |
| Common Use Cases | Used to locate the position of a specific element in a list, often for subsequent operations. |
| Case Sensitivity | Matches elements based on their exact value, including case sensitivity (e.g., ‘A’ ≠ ‘a’). |
| Multiple Occurrences | Returns the index of the first occurrence only. To find all occurrences, use a loop. |
The index() method is a straightforward way to find the position of an element within a Python list, aiding in various list-based operations.
Also Read: How to use list insert in Python
Use cases for Python list index method
Here are some use cases where the Python list index can be useful:
- Finding the position of an element in a list: This is the most common use case for the list.index() method. For example, you could use it to find the position of a student’s name in a list of students or to find the position of a date in a list of birthdays.
- Removing an element from a list by its index: You can use the list.index() method to find the index of an element in a list, and then use the list.remove() method to remove the element at that index. For example, you could use this to remove a student from a list of students or to remove a date from a list of birthdays.
- Slicing a list by its index: You can use the list.index() method to find the index of the start of a slice, and then use the list[start: end] notation to slice the list. For example, you could use this to slice a list of students to get a list of students from a particular class or to slice a list of birthdays to get a list of birthdays from a particular month.
- Sorting a list by its index: You can use the list.sort() method to sort a list, and pass the list.index() method as a key function. This will sort the list based on the index of the elements. For example, you could use this to sort a list of students by their last name or to sort a list of birthdays by their date.
We hope this helps! Let us know if you have any other questions.
Best,
TechBeamers






