One of the common file operations in Python is iterating over files. In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to loop through files in a directory using Python.
Problem: How to Loop Through Files in a Directory
Write a Python program to iterate over files in a directory. This is a pre-requisite for performing operations on files or reading their contents. We often need to iterate over files in a directory.
5 Ways to loop through files in Python
Here are five different solutions to address the above problem. We’ll also compare their advantages and disadvantages at the end.
- Using the
os.listdir()function - Using the
os.scandir()function - Using the
pathlibmodule - Using the
globmodule - Using the
os.walk()function
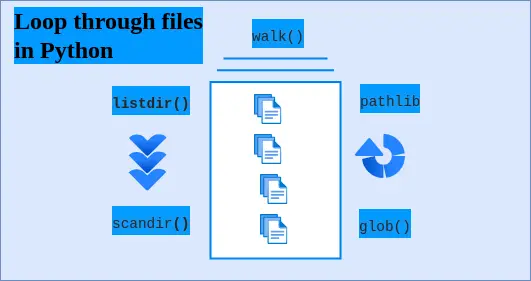
Let us go through the methods and understand how they loop through files in Python inside a directory.
Listdir() function to iterate over files
To loop through files in a directory, you can use os.listdir() to get a list of filenames and then iterate through them.
Python Code:
import os
# Get the current working directory
cwd = os.getcwd()
# Get the list of files in the current directory
files = os.listdir(cwd)
# Loop through the files and print their names
for file in files:
print(file)Also Check: Python List All Files in a Directory
Scandir() function to loop through files
Starting from Python 3.5, the os.scandir() function provides a more efficient way to loop through files and directories.
Python Code:
import os
# Get the current working directory
cwd = os.getcwd()
# Get the list of files in the current directory
files = os.scandir(cwd)
# Loop through the files and print their names
for file in files:
print(file.name)Pathlib module to loop through files
Here’s a complete example of using pathlib to iterate over files in a directory:
Python Code:
from pathlib import Path
# Get the current working directory
cwd = Path.cwd()
# Get the list of files in the current directory
files = cwd.glob('*')
# Loop through the files and print their names
for file in files:
print(file.name)Must Read: Python Glob Example
Python glob() to loop through files
The glob module is excellent for pattern matching and filtering files based on their names. Once the file list is fetched, we can easily loop through files.
Python Code:
import glob
# Get the list of files in the current directory
files = glob.glob('*')
# Loop through the files and print their names
for file in files:
print(file)Walk() function to iterate over files
The os.walk() method is useful when you need to loop through files in subdirectories recursively.
Python Code:
import os
# Get the current working directory
cwd = os.getcwd()
# Walk through the directory tree and print the names of all files
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(cwd):
for file in files:
print(os.path.join(root, file))Must Read: How to Read/Write to a File in Python
Comparison of methods
Here is a brief but to-the-point comparison of different Python ways to iterate over files in a directory.
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
os.listdir() | Simple to use | Does not return file information |
os.scandir() | Returns file information | Slower than os.listdir() |
pathlib | Object-oriented interface | Not as widely used as other methods |
glob | Supports wildcards | Can be difficult to use for complex patterns |
os.walk() | Recursive | Can be slow for large directory trees |
Recommendation
The best method to loop through files in a directory depends on your program requirements. In most cases, the os.listdir() function is the simplest and most efficient option. If file information is needed, the os.scandir() function can be used. The pathlib module provides a more object-oriented interface for working with files and directories. The glob module can be used for matching files with wildcards. The os.walk() function can be used for recursively walking through directory trees.
Also Check: Read File Line by Line in Python
Before You Leave
Looping through files in a directory is a common task in Python. By understanding the different methods available, you can choose the best method for the specific needs of your application.
Lastly, our site needs your support to remain free. Share this post on social media (Linkedin/Twitter) if you gained some knowledge from this tutorial.
Enjoy coding,
TechBeamers.