💡 Want to use SQL in Python effortlessly? This step-by-step guide will show you how to:
✅ Set up SQL in Python and establish a secure database connection
✅ Perform SQL operations in Python – SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
✅ Execute advanced SQL queries with Python – Joins, Transactions, Aggregations
✅ Follow best practices for optimizing database performance
We’ll focus on MySQL, but these techniques also apply to PostgreSQL and SQLite.
🎯 By the end, you’ll understand:
✔️ How Python and SQL work together for database management
✔️ How to run SQL queries with Python effectively
✔️ How to optimize performance using SQL in Python
🔥 Let’s get started with SQL in Python!
- UML Diagram for Using SQL in Python
- Steps to Connect Python with an SQL Database
- Install and Import Python SQL Connector
- Connect SQL in Python and Run Queries
- Python SQL Sequence Diagrams
- Python SQL Database Operations
- Setup MySQL User for Connection
- Common Database Connection Script
- Creating a SQL Database in Python
- Creating SQL Tables in Python
- Insert, Update, Select, and Delete Data
- Check GitHub for More Engaging Stuff
- Quick Summary – Using SQL in Python

UML Diagram for Using SQL in Python
Python’s flexibility makes it easy to connect to various databases, allowing your apps to interact seamlessly with different database systems Below is a simple UML diagram illustrating how to connect Python with a MySQL database.
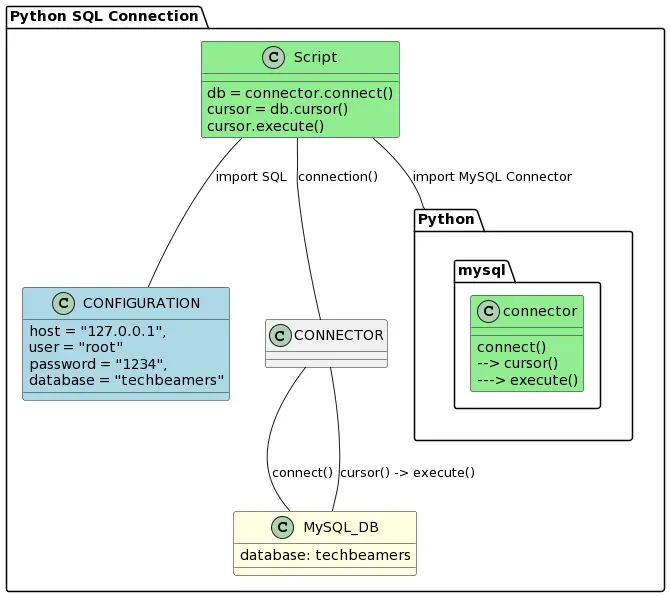
In this tutorial, we will focus on MySQL, though the steps are similar for other databases. To begin, ensure that you have a running MySQL instance. If MySQL isn’t installed, check out our guide on How to Install MySQL on Ubuntu. If MySQL is already set up on your local or remote system, you’re ready to proceed with the next steps.
Also Read: Python MongoDB Tutorial
Steps to Connect Python with an SQL Database
To connect Python with an SQL database, read and follow these steps carefully. They will guide you with what to do and help with any error you might face in between.
Install and Import Python SQL Connector
To start, you need to install a suitable database library, such as mysql-connector-python, pymysql, or sqlite3. You can install the library using pip.
Check if you already have mysql-connector-python installed.
pip list | grep mysql-
If the above command doesn’t show any results, run the following to install the MySQL connector:
pip install mysql-connector-python
Once installed, check if the library was installed correctly:
pip show mysql-connector-python
If you encounter issues with mysql-connector, uninstall it and reinstall mysql-connector-python to avoid conflicts.
pip uninstall mysql-connector pip uninstall mysql-connector-python pip install mysql-connector-python
In your Python script, import the necessary library:
import mysql.connector
Connect SQL in Python and Run Queries
To interact with the database, use the connect() method, providing necessary details like host, user, password, and database.
connection = mysql.connector.connect( host="db_host", user="db_user", password="db_password", database="db_name" )
Our demo Python script will use “temp” as the username and password. The database name is “techbeamers” and “127.0.0.1” is the host. You can however replace the host with the “localhost”.
After establishing the connection, create a cursor object to execute SQL queries.
cursor = connection.cursor()
With the cursor object, you can execute SQL queries.
cursor.execute("SELECT * FROM your_table")If your query returns results, use the cursor to fetch them.
results = cursor.fetchall()
If you make any changes to the database, remember to commit those changes.
connection.commit()
Once done, close the connection to free up resources.
connection.close()
Connecting Python with SQL databases allows seamless integration and offers efficient data management for your applications.
Python SQL Sequence Diagrams
The flow below illustrates the sequence of method calls for connecting Python with an SQL database and interacting with it.
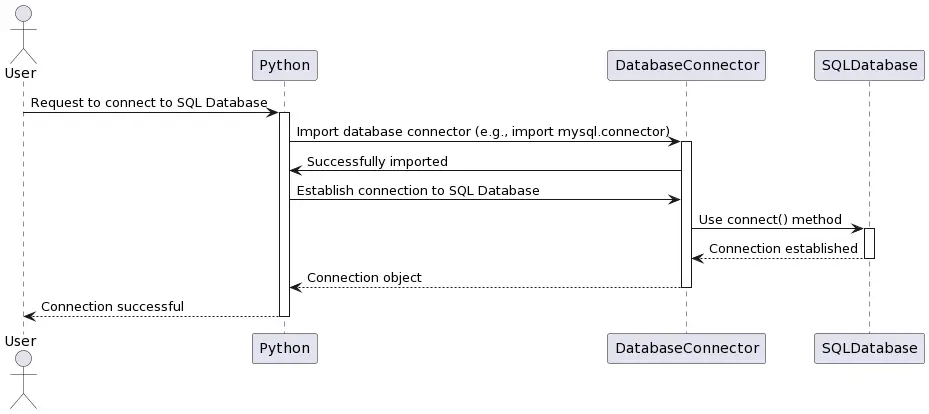
Once connected, you can execute SQL queries and fetch records using the cursor object, as shown in the below diagram.
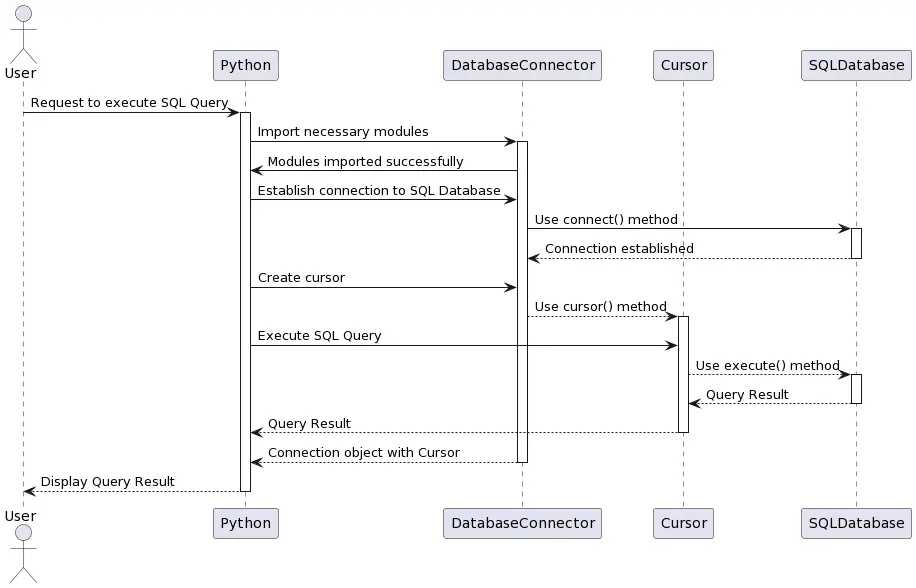
Below is a sequence diagram that covers the full end-to-end flow of how Python connects with the MySQL database. It visually explains how the database connection takes place using Python. Next, it also captures requesting data from the SQL tables using cursors.
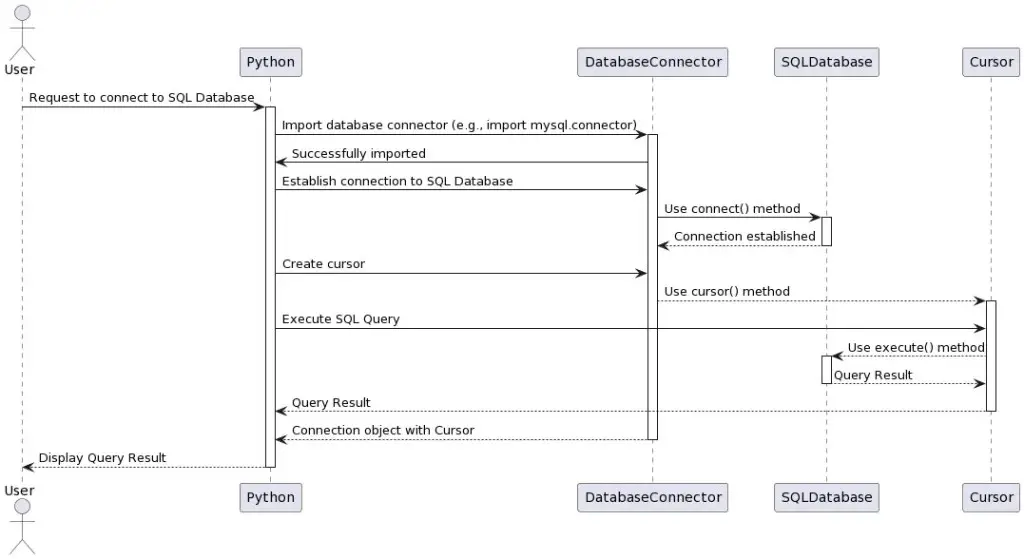
Python SQL Database Operations
So far, you must have thoroughly understood how to set up Python for connecting to a SQL database. The next step is to learn to perform different database operations that can be done using Python.
Setup MySQL User for Connection
Before running the code, create a temporary MySQL user with the necessary privileges.
-- Connect to MySQL with sudo / provide a password if needed sudo mysql -u root -- Create a temporary user with 'mysql_native_password' authentication CREATE USER 'temp'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH 'mysql_native_password' BY 'temp'; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'temp'@'localhost' WITH GRANT OPTION; FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
When you’re done, remove the temporary user to avoid any security risks:
-- Revoke privileges and delete the temporary user
REVOKE ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* FROM 'temp'@'localhost';
DROP USER 'temp'@'localhost';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
The above steps ensure you don’t run into database connection errors when you execute the Python script. However, if it still does, let us know, and we’ll resolve it.
Now, it’s time to get everything we learned and set up to actual action – which means let’s prepare the Python code to connect to an SQL database, create tables, and run different types of queries.
Common Database Connection Script
To reduce redundancy, keep your database connection code in a utility file, db_utils.py, and import it where needed.
# filename: db_utils.py
import mysql.connector
def connect_db(db_name="techbeamers"):
if db_name == "":
# Connect to MySQL server without specifying a database
db = mysql.connector.connect(
host="127.0.0.1",
user="temp",
password="temp"
)
else:
# Reconnect to the specific database
db = mysql.connector.connect(
host="127.0.0.1",
user="temp",
password="temp",
database=db_name
)
return db
def print_separator():
print("*" * 50)By importing this script, you ensure a steady connection for your Python applications, promoting code reuse and keeping things consistent.
Creating a SQL Database in Python
This script demonstrates creating a table inside the database:
from db_utils import *
def create_db(db_name="techbeamers"):
db = connect_db("")
# Create a cursor object to execute SQL queries
cur = db.cursor()
# Create the database if it doesn't exist
cur.execute(f"CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS {db_name}")
# Close the cursor
db.close()
print_separator()
print(f"Database created as {db_name}")
# Call the function create the database
create_db()Creating SQL Tables in Python
This script demonstrates creating a table inside the database:
from db_utils import *
# Create tables
def create_tables():
db = connect_db()
cur = db.cursor()
# Create 'clients' table
cur.execute("CREATE TABLE clients (id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR(255), address VARCHAR(255))")
print_separator()
print("Table 'clients' created")
# Create 'orders' table
cur.execute("CREATE TABLE orders (order_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, client_id INT, product VARCHAR(255))")
print_separator()
print("Table 'orders' created")
# Create 'products' table
cur.execute("CREATE TABLE products (product_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR(255), price DECIMAL(10, 2))")
print_separator()
print("Table 'products' created")
db.commit()
# Call the function create the tables
create_tables()Insert, Update, Select, and Delete Data
For basic data operations such as inserting, updating, and deleting data, here’s a general approach.
Insert Data:
from db_utils import *
# Insert dummy data
def insert_data():
db = connect_db()
cur = db.cursor()
# Insert data into 'clients' table
sql_clients = "INSERT INTO clients (name, address) VALUES (%s, %s)"
val_clients = [("Jason Woo", "103 Main St"), ("Alice Johnson", "201 Oak Ave")]
cur.executemany(sql_clients, val_clients)
print_separator()
print("Data inserted into 'clients' table")
# Insert data into 'orders' table
sql_orders = "INSERT INTO orders (client_id, product) VALUES (%s, %s)"
val_orders = [(1, "Laptop"), (2, "Phone"), (1, "Tablet")]
cur.executemany(sql_orders, val_orders)
print_separator()
print("Data inserted into 'orders' table")
# Insert data into 'products' table
sql_products = "INSERT INTO products (name, price) VALUES (%s, %s)"
val_products = [("Laptop", 999.99), ("Phone", 499.99), ("Tablet", 299.99)]
cur.executemany(sql_products, val_products)
print_separator()
print("Data inserted into 'products' table")
db.commit()
# Call the function insert dummy data
insert_data()Select Data:
Now, let’s retrieve data. This script connects to the database, selects all records from the “clients” table, and prints the results.
from db_utils import *
def select_data(tbl_name="clients"):
db = connect_db()
cur = db.cursor()
cur.execute(f"SELECT * FROM {tbl_name}")
myresult = cur.fetchall()
print_separator()
print(f"Selecting data from {tbl_name}")
for row in myresult:
print(row)
# Call the function to fetch records
select_data()Update Data:
Updating records is a breeze. Connect to the database and modify the address for the client with ID 1 in the “clients” table.
from db_utils import *
# Update data in 'clients' table
def update_data(tbl_name="clients"):
db = connect_db()
cur = db.cursor()
# Update address for the client with ID 1 in the 'clients' table
sql_update = f"UPDATE {tbl_name} SET address = '456 Oak St' WHERE id = 1"
cur.execute(sql_update)
print_separator()
print(f"Data updated in '{tbl_name}' table")
db.commit()
# Call the function to update data
update_data()These Python snippets guide you through basic SQL operations, making it easy to manage databases with Python. Remember to keep the common database connection code in a separate file for reusability.
Join Tables:
Combining data from different tables is seamless with Python SQL Join operations. Import our common connection script, connect to the database, and execute a JOIN query to fetch related data from multiple tables.
from db_utils import *
# Perform SQL JOIN operation
def sql_join_ops():
db = connect_db()
cur = db.cursor()
# Example of INNER JOIN
cur.execute("SELECT clients.name, orders.product FROM clients INNER JOIN orders ON clients.id = orders.client_id")
result = cur.fetchall()
print_separator()
print("Results of SQL JOIN operation:")
for row in result:
print(row)
# Call the function to update data
sql_join_ops()Aggregate Data:
Aggregating data with Python enhances data analysis. Sum, average, and count functions are pivotal.
from db_utils import *
# Perform SQL Aggregate Functions
def sql_aggr_ops():
db = connect_db()
cur = db.cursor()
# Sum
cur.execute("SELECT SUM(price) FROM products")
sum_result = cur.fetchone()[0]
print_separator()
print("Sum of prices in 'products' table:", sum_result)
# Average
cur.execute("SELECT AVG(price) FROM products")
avg_result = cur.fetchone()[0]
print_separator()
print("Avg price in 'products' table:", avg_result)
# Count
cur.execute("SELECT COUNT(*) FROM products")
count_result = cur.fetchone()[0]
print_separator()
print("No. of records in 'products' table:", count_result)
# Call the above method to demo mysql aggregate functions
sql_aggr_ops()This Python code demonstrates how to leverage SQL aggregate functions to perform calculations on your data. Sum, average, and count functions offer valuable insights into your dataset’s characteristics.
Delete Tables:
Deleting a table is straightforward in Python. Connect to the database and remove the “clients” table.
from db_utils import *
def drop_table(table_name):
db = connect_db()
cur = db.cursor()
# Drop the given table if it exists
cur.execute(f"DROP TABLE IF EXISTS {table_name}")
print_separator()
print(f"Table '{table_name}' dropped")
db.commit()
db.close()
# Call the above method to drop the table
drop_table()Delete Database:
Deleting a database is as simple as creating one. Connect to the server and drop the “techbeamers” database.
from db_utils import *
def drop_db(db_name="techbeamers"):
db = connect_db()
cur = db.cursor()
# Drop the given database if it exists
cur.execute(f"DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS {db_name}")
print_separator()
print(f"Database '{db_name}' dropped")
db.close()
# Call the above method to drop the database
drop_db()The above two Python examples showcase how to delete tables and databases using Python. With these operations, you get flexibility in managing your database structures. However, always be responsible and mindful when performing delete operations to avoid unintentional data loss.
Check GitHub for More Engaging Stuff
Please note that all the above examples after thorough testing are carefully published to the following GitHub repo: https://github.com/techbeamers/python-sql-examples
Here you can find the examples saved in the form of Python scripts. In addition, you will get scripts related to dedicated DB operation with a launcher script and a single Python script to run and test the whole stuff.
Quick Summary – Using SQL in Python
This tutorial has made it easy to connect Python with an SQL database and perform basic operations. To go further, practice with the examples provided and start integrating them into your own projects.
The Python scripts shared are practical and effective, showcasing key SQL commands. Keep your Python SQL projects simple by leveraging these examples for efficient database management.
If you found this tutorial helpful, share this post on social media and subscribe to our YouTube channel for more tutorials.
Happy Coding,
TechBeamers.





