Understand the differences between Shallow Copy and Deep Copy (Shallow Copy vs. Deep Copy) in Python. These are core programming concepts and you should know how copy works behind the scenes.
Note: The syntax used in the below section is for Python 3. You may change it to use a different version of Python.
Shallow Copy vs. Deep Copy
Must Read – 9 Ways to Copy a File in Python
The difference between shallow and deep copy
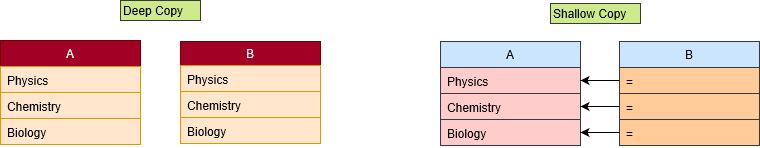
A shallow copy operation creates a new object that stores the reference of elements of the original object. So, any changes in the new object also affect the original and vice versa.
While, in deep copy, the new object stores the copy of all elements of the original object. Thus, the result is a fresh list separate from the original one. Hence, it can be changed without affecting the original object.
In summary, when you change the deep copy of a list, the old list remains as is. But shallow copy causes changes in both the new and the old list.
The diagram below represents the difference between the shallow and the deep copy.
How to perform a shallow and deep copy?
When creating a shallow copy, use the assignment operator(=) to create them.
With the Copy module, you can create a shallow copy using the below syntax:
import copy copy.copy(object_name)
For a deep copy, the following code can be used:
import copy copy.deepcopy(object_name)
In the next section, a few programs are implemented to demonstrate the Copy Module in Python 3.
Understand by examples
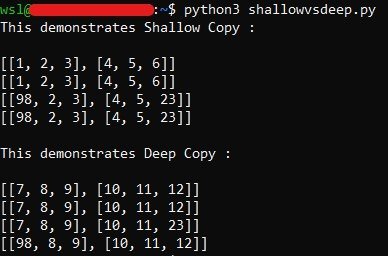
Here is a simple program to demonstrate the difference between Shallow and Deep copy.
import copy
a = [ [1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6] ]
b = copy.copy(a)
c = [ [7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12] ]
d = copy.deepcopy(c)
print(a)
print(b)
a[1][2] = 23
b[0][0] = 98
print(a)
print(b)
print("\n")
print(c)
print(d)
a[1][2] = 23
b[0][0] = 98
print(c)
print(d)
The output will come as:
Key differences
Here is a table summarizing the key differences between shallow copy and deep copy in Python:
| Feature | Shallow Copy | Deep Copy |
|---|---|---|
| What it does | Creates a new object that references the same objects as the original object. | Creates a new object that contains copies of all the objects referenced by the original object. |
| When to use it | When you only need to copy the top-level structure of an object. | When you need to copy the entire object hierarchy, including nested objects. |
| Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Memory usage | Less memory-intensive | More memory-intensive |
| Availability | Available in the standard library | Requires the copy module |
The following are some more topics which could be of interest to you. Please check them out.
Python vs C++ – Understand the Differences
Python Sets vs Lists – Check Out the Differences
Generators vs List Comprehensions in Python
Map vs List Comprehension Difference
Difference Between List Append and Extend
Python XRange vs Range Differences
Summary
Here is a simple explanation of each feature:
We hope this helps! Let us know if you have any other questions.
Lastly, our site needs your support to remain free. Share this post on social media (Linkedin/Facebook) if you gained some knowledge from this tutorial.
Enjoy coding,
TechBeamers.