In this tutorial, we will explore the top-down approach in the context of C programming. We will cover the key concepts, benefits of this approach, and how to implement it. Additionally, we will provide unique code examples to illustrate the principles of the top-down approach.
Understand the top-down approach
The top-down approach to programming in C has a long history, dating back to the early days of the language. It was first popularized by Niklaus Wirth, the creator of the Pascal language. Wirth argued that the top-down approach was the most efficient and effective way to develop complex software.
What is a top-down approach in C?
A top-down approach is a logical way of programming that first divides a large problem into smaller, more manageable pieces. Subsequently, It ensures that each piece has a desirable solution. Finally, all solutions form together to solve the original problem. Given these points, the coding fraternity often calls this approach by the name “Subproblem Reduction”.
Try This: Java Programming Practice Test
Pros and Cons of the top-down approach
This approach is quite useful in some cases but also lacks in a few. However, let’s see how the pros precede the cons.
Advantages
The top-down approach has several advantages, including:
- It makes complex problems easier to solve by breaking them down into smaller, more manageable pieces.
- It makes programs more modular and reusable by separating the sub-problems and solving them independently of each other.
- It makes programs easier to debug by ensuring the sub-problems go through testing individually.
- It makes programs easier to maintain, as changes to one sub-problem are less likely to affect other parts of the program.
Disadvantages
- One disadvantage of the top-down approach is that it can be difficult to design an efficient solution to a problem without first understanding the details of the sub-problems.
- Another disadvantage is that the top-down approach can lead to redundancy if the same code appears in multiple sub-problems.
How to use the top-down approach in C
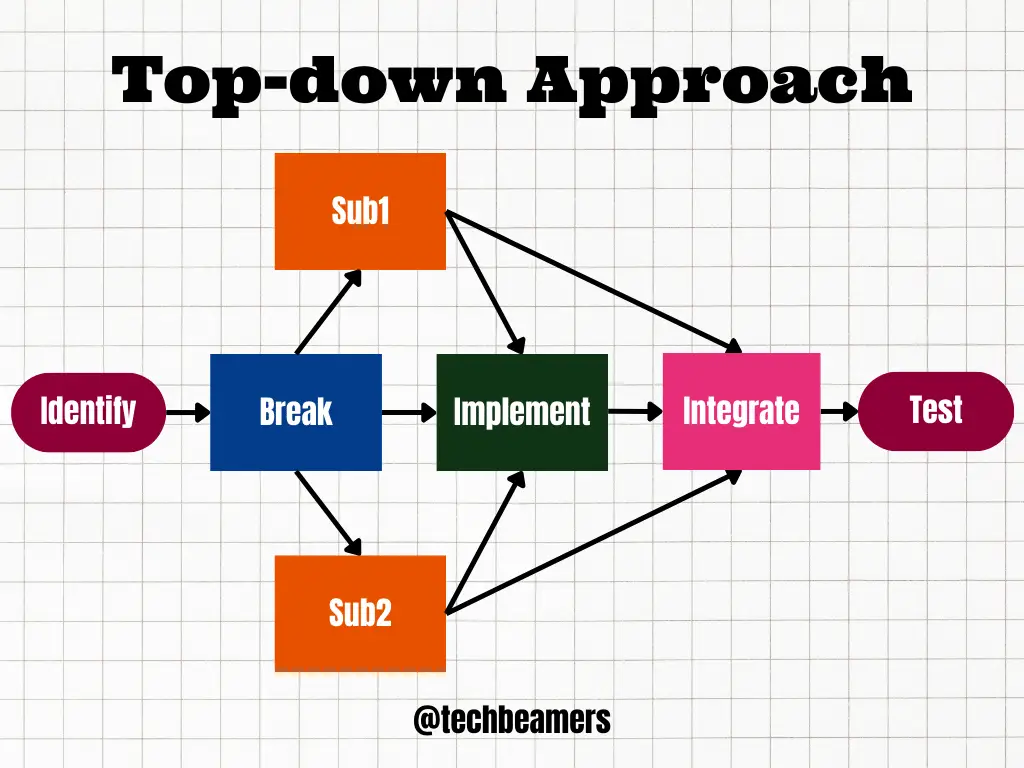
To use the top-down approach in C, you can follow these steps:
- Identify the problem. What are the inputs and outputs of the program? What is the desired functionality?
- Break the problem down into sub-problems. What are the major tasks that the program needs to perform? Can we divide these tasks further into smaller sub-tasks?
- Implement each sub-problem in a separate function. This will make the program more modular and reusable.
- Call the sub-functions from the main function. The main function should simply orchestrate the execution of the sub-functions.
- Test and debug the program. Make sure that each sub-problem gets a correct solution, and that the overall program works as expected.
Test Yourself: Best Python Programming Online Test
Example code snippet
The following code snippet shows a simple example of the top-down approach in C:
C code:
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to find the factorial of a number
int fact(int n) {
if (n == 0) return 1;
return n * fact(n - 1);
}
// Function to find the square of a number
int sqr(int x) {
return x * x;
}
// Function to find the cube of a number
int cube(int x) {
return x * x * x;
}
// Main function
int main() {
int num;
// Get input from the user
printf("Enter a number: ");
scanf("%d", &num);
// Find the factorial, square, and cube of the number
int fact_result = fact(num);
int sqr_result = sqr(num);
int cube_result = cube(num);
// Display the results to the user
printf("Factorial: %d\n", fact_result);
printf("Square: %d\n", sqr_result);
printf("Cube: %d\n", cube_result);
return 0;
}The above C code follows the top-down approach:
- It divides the logic into smaller tasks (finding the square, factorial, and cube of a number and printing the result).
- Each task has a separate function to work.
- The data flows through the functions in a logical and precise manner.
Develop a C program using the top-down approach
When creating a top-down solution to a problem, it is important to consider the following factors:
- Modularity: The solution should boil down into modules, each of which performs a specific task. This will make the code more reusable and easier to maintain.
- Abstraction: The solution should hide the implementation details of each module from the other modules. This will make the code more concise and easier to understand.
- Data flow: The solution should use a design that implements a logical and efficient data flow across the modules.
To demonstrate the concept of a top-down approach, let’s code the following problem in C.
Problem statement
Problem: To develop a system to store and manage student information, including student ID, name, grades, and average grade. The system should be able to print the details of a student, find the highest grade of a student, and calculate the average grade of a student.
Solution: We’ll use the top-down approach to solve this problem. Firstly, the process will start by dividing the problem into sub-problems, such as:
- Designing a data structure to store student information
- Implementing functions to add, delete, and update student information
- Implementing functions to print the details of a student, find the highest grade of a student, and calculate the average grade of a student
- Developing a user interface to interact with the system
Source code of the C program
The following code snippet shows a more complex example of the top-down approach in C:
C code:
#include <stdio.h>
// Struct to keep student info
typedef struct {
int roll_number;
char name[50];
int marks[3];
float average;
} student;
// Function to find the avg marks of a student
float find_avg(student *std) {
float avg = 0.0;
for (int ix = 0; ix < 3; ix++) {
avg += std->marks[ix];
}
return avg / 3.0;
}
// Function to print the details of a student
void print_std_info(student *std) {
printf("Roll number: %d\n", std->roll_number);
printf("Name: %s\n", std->name);
printf("Marks: %d, %d, %d\n", std->marks[0], std->marks[1], std->marks[2]);
printf("Average: %f\n", std->average);
}
// Main function
int main() {
student std1;
// Get input from the user
printf("Enter the student's roll number: ");
scanf("%d", &std1.roll_number);
printf("Enter the student's name: ");
scanf("%s", std1.name);
printf("Enter the student's marks: ");
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
scanf("%d", &std1.marks[i]);
}
// Calculate the student's average marks
std1.average = find_avg(&std1);
// Print the student's details
print_std_info(&std1);
return 0;
}This code snippet is a bit more complex than the previous example. However, it illustrates the key concepts of the top-down approach in C:
- The problem (Find out the average marks of a student) is divided into smaller modules (Get the sum of the marks and divide it by 3).
- Each module performs a specific task and hides its implementation details from the other modules.
- The data flow should be logical and efficient across the modules.
Tips – How to quickly adapt the top-down approach
Here are some tips for using the top-down approach effectively:
- Start by creating a high-level design of the solution. This will help you to understand the overall structure of the program and the relationships between the different modules.
- Use pseudocode to describe the functionality of each module. This will help you to refine your design and identify any potential problems.
- Implement the modules one at a time. This will make it easier to test and debug the program.
- Use unit testing to test each module individually. This will help you to identify and fix any bugs early on.
- Use integration testing to test the modules together. This will help you to identify any bugs that arise when the modules are integrated.
Check This: SQL Programming Test with 20+ Queries
Comparison of different approaches
The following table compares the top-down and bottom-up approaches:
| Characteristic | Top-down approach | Bottom-up approach |
|---|---|---|
| Starts with | Overview of the problem | Individual components of the problem |
| Progresses by | Breaking the problem down into smaller sub-problems | Combining individual components to form larger components |
| Ends with | A complete solution to the problem | A working prototype of the system |
| Suitable for | Complex problems | Simple problems |
Differences in a 3-D view
Let’s look at the differences in a 3-D view.
| Approach | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Top-Down | Promotes modularity and clarity | Initial setup may take longer |
| Bottom-Up | Focuses on faster development | Face integration challenges |
| Iterative | Adaptable to changes in requirements | Result in frequent changes and refactoring |
Which approach is the most suitable?
The most suitable approach for a particular problem depends on the complexity of the problem and the experience of the programmer. For complex problems, the top-down approach is generally preferred, as it makes the problem easier to solve and maintain. For simple problems, the bottom-up approach may be more efficient, as it allows the programmer to start working on the solution immediately.
Conclusion: Top-down approach in C
The top-down approach is a powerful method that can be used to solve complex problems. It deems fit for problems that can be naturally divided into smaller sub-problems. By using the top-down approach, programmers can write more modular, reusable, and extensible code.
In conclusion, the top-down approach in C programming is an excellent choice for projects and a desire for maintainable, modular code. By following the steps outlined in this tutorial, you can develop well-structured C programs that are easy to manage and extend.
Lastly, our site needs your support to remain free. Share this post on social media (Linkedin/Twitter) if you gained some knowledge from this tutorial.
Happy coding,
TechBeamers.






