In MySQL, you might wonder what’s the difference between UPSERT and INSERT commands. The INSERT clause adds new rows into a table. It only puts new data and does not change any old data. On the other hand, the UPSERT does two jobs. It adds new rows, but if a row with the same key already exists, it updates that row. This helps to keep data correct and stops duplicates.
Understand the Difference Between UPSERT & INSERT
Here is the main difference between UPSERT and INSERT in MySQL:
- INSERT adds only new rows.
- UPSERT adds new rows or updates old rows if they are there.
- INSERT gives error when duplicate row comes.
- UPSERT solves this by updating the existing row.
- The syntax for INSERT is simple — you write new values.
- For UPSERT, MySQL uses
INSERT ... ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATEto add or update data.
To finish, INSERT adds new data only, and UPSERT adds or updates data in MySQL tables. UPSERT is very helpful to keep your data clean and right.
Below is a simple diagram to show the difference between UPSERT and INSERT.
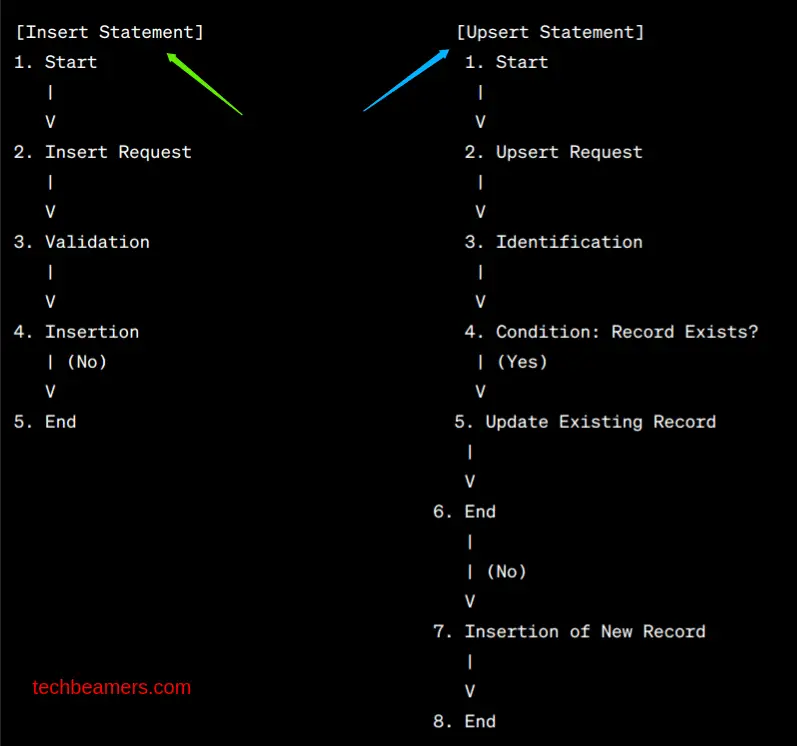
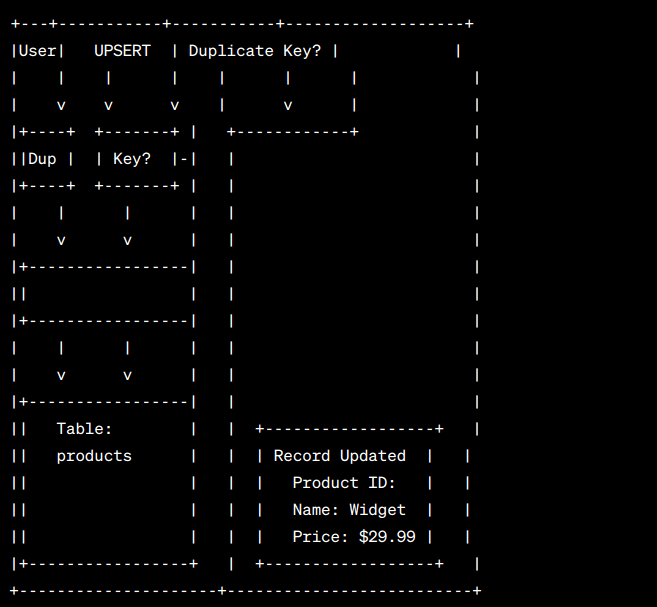
Next, we’ve specifically placed another picture showing how the Upsert statement works in MySQL.
Examples to Show Difference Between UPSERT & INSERT
Let us see some simple examples to understand how UPSERT and INSERT work in MySQL. These examples help you know the difference clearly.
UPSERT Examples
Example 1: You have a table called products. The product_code must be unique for each product. You want to add a new product or change price if the product is already in the table. UPSERT is best here.
MySQL code:
INSERT INTO products (product_code, product_name, price)
VALUES ('P001', 'Wireless Mouse', 25.99)
ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE price = VALUES(price);This UPSERT adds new product if P001 is not in the table yet. If product P001 is there, it updates price.
Example 2: You have a users table with unique username and email. When a user signs up or changes password, UPSERT helps add or update info without duplicate.
MySQL code:
INSERT INTO users (username, email, password)
VALUES ('john_doe', 'john@example.com', 'securePass123')
ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE password = 'securePass123';This UPSERT adds new user if username or email is new. If user exists, it updates password.
INSERT Examples
Example 1: You have an employees table. Each employee has a unique ID. When hiring new employee, you add details. INSERT is good here.
MySQL code:
INSERT INTO employees (employee_id, name, position)
VALUES (101, 'Alice Smith', 'Marketing Manager');This INSERT adds new employee record. No duplicate problem because employee ID is unique.
Example 2: You have a sales table for sales data. Each sale has unique sale ID. When new sale happens, you add it with INSERT.
MySQL code:
INSERT INTO sales (sale_id, amount, sale_date)
VALUES ('S1001', 199.99, '2025-08-16');This INSERT adds new sale record without checking duplicates.
Simple Thumb Rules for UPSERT and INSERT
INSERT is simple and good when you add new data and no duplicates come. UPSERT is useful because it adds new data or updates old data if already there. UPSERT helps keep MySQL data clean and right.
When to Use UPSERT
Use UPSERT when:
- You want data always up to date.
- You want to stop duplicate data in database.
- You want one command to add or update row, even if row not there before.
When to Use INSERT
Use INSERT when:
- You know new row is not in database.
- You want to add many rows at once.
- You want to add new data only, no change old data.
Key Points: UPSERT vs INSERT — What It Means
- INSERT adds new rows in MySQL table. It works well when data is new and no duplicates.
- UPSERT tries to add new rows, but if row with same key exists, it updates that row. This keeps data clean and avoids error.
- Use UPSERT when you expect duplicates or want to update existing data. Use INSERT when you only add new data without updates.
Check out the different ways to perform the UPSERT operation in MySQL.
We need your support to run this blog, so share this post on your social media accounts like Facebook / Twitter. This is how you will encourage us to come up with more informative stuff.
Happy learning!







Looking forward to your next post. Keep up the good work!
Thanks for the valuable suggestion. We’ll update accordingly in sometime.
You might want to go a bit deeper into these are UPSERT “operations” and that there is no actual command “UPSERT” you are going to type.
I think a good way to describe it would be……. It’s an UPSERT operation using the INSERT command with a ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE clause.
INSERT INTO products (product_code, product_name, price) VALUES ('P001', 'Widget A', 73.13) ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE price = 73.13; INSERT INTO users (username, email, password) VALUES ('hello_world', 'hello@world.com', 'new_secure_pass') ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE password = 'new_secure_pass';